
The 555 timer IC was introduced in the year 1970 by Signetic Corporation and gave the name SE/NE 555 timer. It is basically a monolithic timing circuit that produces accurate and highly stable time delays or oscillation. When compared to the applications of an op-amp in the same areas, the 555IC is also equally reliable and is cheap in cost. Apart from its applications as a monostable multivibrator and astable multivibrator, a 555 timer can also be used in dc to dc converters, digital logic probes, waveform generators, analog frequency meters and tachometers, temperature measurement and control devices,voltage regulators etc. The timer IC is setup to work in either of the two modes – one-shot or monostable or as a free-running or astable multivibrator. The SE 555 can be used for temperature ranges between – 55°C to 125°. The NE 555 can be used for a temperature range between 0° to 70°C.
The important features of the 555 timer are :
⇒ It operates from a wide range of power supplies ranging from + 5 Volts to + 18 Volts supply voltage.
⇒ Sinking or sourcing 200 mA of load current.
⇒ The external components should be selected properly so that the timing intervals can be made into several minutes along with the frequencies exceeding several hundred kilo hertz.
⇒ The output of a 555 timer can drive a transistor-transistor logic (TTL) due to its high current output.
⇒ It has a temperature stability of 50 parts per million (ppm) per degree Celsius change in temperature, or equivalently 0.005 %/ °C.
⇒ The duty cycle of the timer is adjustable.
⇒ The maximum power dissipation per package is 600 mW and its trigger and reset inputs has logic compatibility.
MODES OF OPERATIONS:
1. Astable mode
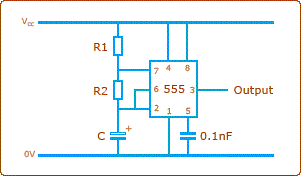
An Astable Circuit has no stable state - hence the name "astable". The output continually switches state between high and low without without any intervention from the user, called a 'square' wave. This type of circuit could be used to give a mechanism intermittent motion by switching a motor on and off at regular intervals. It can also be used to flash lamps and LEDs, and is useful as a 'clock' pulse for other digital ICs and circuits.
2. Monostable mode
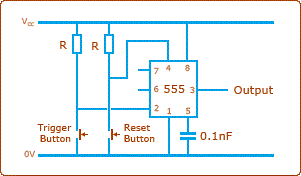
A Bistable Mode or what is sometimes called a Schmitt Trigger, has two stable states, high and low. Taking the Trigger input low makes the output of the circuit go into the high state. Taking the Reset input low makes the output of the circuit go into the low state. This type of circuit is ideal for use in an automated model railway system where the train is required to run back and forth over the same piece of track. A push button (or reed switch with a magnet on the underside of the train) would be placed at each end of the track so that when one is hit by the train, it will either trigger or reset the bistable. The output of the 555 would control a DPDT relay which would be wired as a reversing switch to reverse the direction of current to the track, thereby reversing the direction of the train.
Category:




