INTRODUCTION
The computer numerical control (CNC) facilitates integration of various manufacturing operations, provides flexibility to accommodate the design changes and reduces the human error thereby increasing the safety level in the manufacturing floor. In addition, CNC results in high accuracy and short production time. The drawbacks include high cost, maintenance, and the requirement of skilled part programmer.It is the technology of controlling a machining operation using a computer program, which is called Numerical Control (NC) Program. In other words, a computer rather than a person will directly control the machine tool.
CNC falls under the category of "Automation" which is defined as the process of performing a sequence of operations with little or no human effort using specialized equipment and devices. There are two types of automation: hard and soft. Hard or fixed automation is the design of mass-production machines to produce a standardized product such as an engine block. It is not flexible enough to modify the shapes and dimensions to a large extent. Soft of flexible automation is a process of using numerical control, adaptive control or robotic control to control the various functions of the machine. It produces parts with complex shapes and leads to the development of flexible manufacturing systems. Design changes can readily be implemented in soft automation.
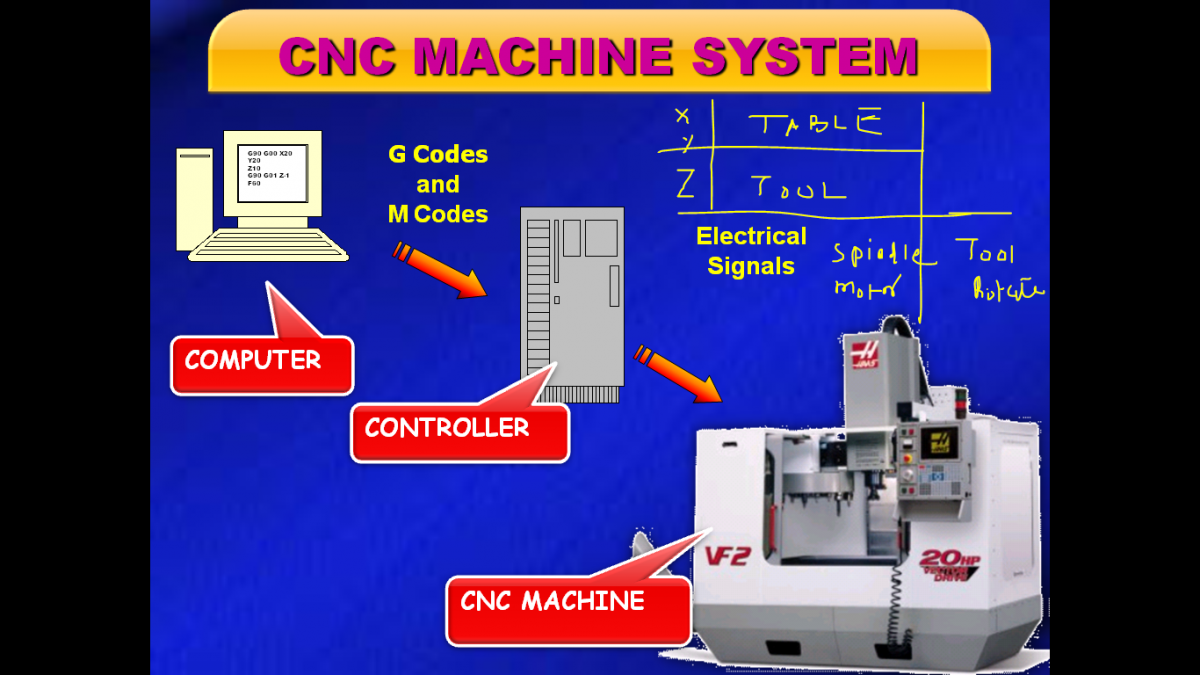
CNC is a method of controlling the functions and motions of a machine tool by means of a prepared program containing instructions in the form of numerical data (numbers and letters). In the field of machining, where CNC has been applied to a large extent, CNC controls the motion of the workpiece of tool, the input parameters such as feed, depth of cut, speed, and the functions such as spindle on/off and coolant on/off.
The applications of CNC included both for machine tool as well as non-machine tool areas. In the machine tool category, CNC is widely used for lathe, drill press, milling machine, grinding unit, laser, sheet-metal press working machine, and tube bending machine. Highly automated machine tools such as turning center and machining center which change the cutting tools automatically under CNC control have been developed. In the non-machine tool category, CNC applications include welding machines (arc and resistance), coordinate measuring machine, electronic assembly, tape laying and filament winding machines for composites.
Category:




